Written by Elizabeth Burns
Cellulite
Cellulite is often known as a skin alteration often described as an ‘orange peel,’ or a 'dimpling' appearance on the thighs, buttocks and sometimes lower abdomen of women and rarely men. Although some men may get it, 95% of cellulite occurs in women. Today we'll discuss everything you need to know about the following topic.
What is Cellulite?
To better understand what cellulite is, let’s begin this explanation with a review of skin anatomy. The outermost layer of skin is referred to as your epidermis. Immediately under this is the dermis, which is richly filled with hair follicles, sweat glands, blood vessels, nerve receptors and connective tissue. The next layer of tissue is the first of three layers of subcutaneous (which means beneath the skin) fat. This is where our discussion will keenly focus in describing cellulite. This uppermost layer of subcutaneous fat has been described as “standing fat-cell chambers” separated by connective tissue. From these fat-cell chambers, small projections of fat cells protrude into the dermis. This unevenness and irregularity of the subcutaneous fat gives skin the ‘bumpy’ appearance we call cellulite.
The reason cellulite is rarely seen in men is because the epidermis, dermis and uppermost part of the subcutaneous tissue is different in males. Men have thicker epidermis and dermis tissue layers in the thighs and buttocks. More distinctly dissimilar, the first layer of fat, which is slightly thinner in men, is assembled into polygonal units separated by crisscrossing connective tissue.
The differences in subcutaneous fat cell structure in men and women occur during the third trimester of fetus development and are manifested at birth. Variations in hormones between genders largely explain this skin structure deviation
Why Does Cellulite Tend to Get Worse as You Age?
In women, the dermis reaches its maximal thickness at 30 years of age. Secondly, the dermis area, which is bound together by the connective tissue starts to get looser, due to the aging process of the collagen and elastic fibers. This allows for more adipose cells to protrude into the dermis area, accentuating the sight of cellulite. In addition, an increased deposition of subcutaneous body fat may often reflect a lifestyle of less exercise and changes in dietary consumption.
Treatments Options?
To reduce the appearance you should start by cleaning up your diet and exercising. Focus on strengthening and working out the areas that show cellulite. For example, if it's on your upper thighs, focus on your glute and thigh exercises.
Of course you could also do CIT or dermarolling as that triggers collagen regrowth, which will smooth over the uneven dimpling of cellulite.
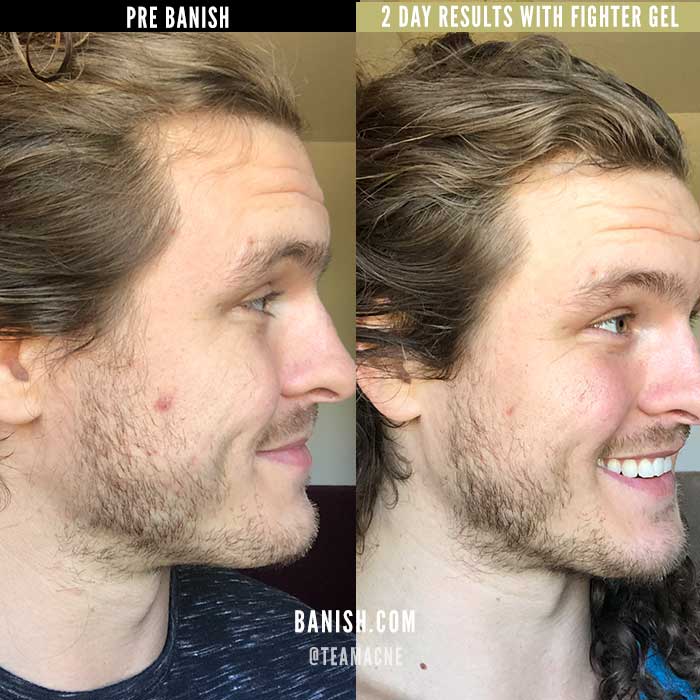










Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.